Recombinant Mouse Fatty acid-binding protein, liver protein (Fabp1)
In Stock-
中文名稱:小鼠Fabp1重組蛋白
-
品名簡稱:Recombinant Mouse Fabp1 protein (Active)
-
貨號:CSB-AP000551MO
-
說明書:
-
規(guī)格:¥852
-
圖片:
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
純度:>95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
內(nèi)毒素:Less than 1.0 EU/μg as determined by LAL method.
-
生物活性:Fully biologically active when compared to standard. The binding affinity of rMuFABP1 for the synthetic ligand cis-parinaric acid has been measured by fluorescence titration. Half maximal fluorescence of 2.5 μM rMuFABP1 is achieved with approximately 5 μM cis-paranaric acid.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Fabp1; FabplFatty acid-binding protein; liver; 14 kDa selenium-binding protein; Fatty acid-binding protein 1; Liver-type fatty acid-binding protein; L-FABP
-
種屬:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白長度:Full Length
-
來源:E.Coli
-
分子量:14.2 kDa
-
表達(dá)區(qū)域:1-127aa
-
氨基酸序列MNFSGKYQLQ SQENFEPFMK AIGLPEDLIQ KGKDIKGVSE IVHEGKKIKL TITYGPKVVR NEFTLGEECE LETMTGEKVK AVVKLEGDNK MVTTFKGIKS VTELNGDTIT NTMTLGDIVY KRVSKRI
-
蛋白標(biāo)簽:Tag-Free
-
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
-
緩沖液:Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered concentrated solution in PBS, pH 7.4, 2 % trehalose.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:5-10 business days
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Plays a role in lipoprotein-mediated cholesterol uptake in hepatocytes. Binds cholesterol. Binds free fatty acids and their coenzyme A derivatives, bilirubin, and some other small molecules in the cytoplasm. May be involved in intracellular lipid transport.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- https://chalkbeat.org/posts/ny/2018/06/04/a-chalkbeat-cheat-sheet-the-specialized-high-schools-admissions-test-overhaul/ PMID: 28972119
- Ablating both Fabp1 and Scp2/Scpx (TKO) induces hepatic phospholipid and cholesterol accumulation in high fat-fed mice PMID: 29307784
- role of Fabp1/Scp-2 in hepatic phytol metabolism PMID: 28411199
- Individually ablating SCPx or SCP2/SCPx elicited concomitant upregulation of L-FABP. PMID: 27940000
- Lack of a significant decrease in the flux of HDL-[(3)H]CE to biliary FC or bile acids in FABP1(-/-) mice indicates the likely compensation of its function by an as yet unidentified mechanism. Taken together, these studies demonstrate that FABP1 and SCP2 facilitate the preferential movement of HDL-CEs to bile for final elimination PMID: 27381048
- data showed that Fabp1 gene ablation markedly diminished the impact of high-fat diet on brain endocannabinoid levels, especially in male mice PMID: 27861894
- Studies show that despite overall tertiary structure similarity, the hFABP1 differs significantly from rat FABP1 in secondary structure, much larger ligand binding cavity, and affinities/specificities for some ligands. Moreover, while both mouse and hFABP1 mediate ligand induction of PPARA, they differ markedly in genes induced. PMID: 27117865
- FABP1 knockout increased brain levels of arachidonic acid-containing endocannabinoids PMID: 27167970
- L-FABP was more important in hepatic retention of bile acids, while SCP-2/SCP-x more broadly affected biliary bile acid and phospholipid levels. PMID: 26541319
- These findings suggest that some of the phenotypic divergence between the two L-Fabp(-/-) lines may reflect unanticipated differences in genetic background, underscoring the importance of genetic background in phenotypic characterization. PMID: 26251469
- Loss of L-FABP and SCP-2, or both induces hepatic lipid accumulation in female mice and mimics non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PMID: 26116377
- attenuates tubulointerstitial damage in aldosterone-induced nephropathy by reducing oxidative stress PMID: 25339700
- L-FABP appears to function more in hepatic retention of bile acids as well as hepatic uptake and biliary secretion of HDL-cholesterol PMID: 25277800
- L-FABP is not required to channel ATGL-hydrolyzed FAs to mitochondria for beta-oxidation or the nucleus for PPAR-alpha regulation PMID: 24610891
- Data show that combined deletion of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (Mttp) and liver fatty acid binding protein 1 (L-Fabp) are protected from lithogenic diet (LD)-induced gallstone formation. PMID: 24474819
- L-Fabp has a role in modifying intestinal fatty acid composition and adenoma formation in ApcMin/+ mice PMID: 23921281
- The maximum increase in LFABP expression occurs when stimulation with IL-6 and PPARalpha-ligands takes place simultaneously. PMID: 23534555
- liver-type fatty acid-binding protein in the proximal tubules may protect against angiotensin II-induced SSHT by attenuating activation of the intrarenal renin-angiotensin system and reducing oxidative stress and tubulointerstitial inflammation. PMID: 23940201
- These data establish that L-FABP is an indirect antioxidant protein essential for sequestering FFA and that its impairment could contribute to in the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease . PMID: 23359610
- CrPic exhibited amelioration alloxan induced oxidative stress in mouse livers. A significant increase in liver fatty acid-binding protein (L-FABP) was observed, which indicates increased fatty acid utilization in liver tissue PMID: 23603011
- Liver-type fatty acid-binding protein gene-ablation exacerbated diet-induced weight gain and fat tissue mass gain in mice fed high-fat diet. PMID: 23539345
- L-FABP deletion attenuates both diet-induced hepatic steatosis and fibrogenesis, despite the observation that L-Fabp paradoxically promotes fatty acid and lipid droplet accumulation and inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation in vitro. PMID: 23401290
- L-FABP's importance in fibrate-induction of hepatic PPARalpha LCFA beta-oxidative genes, especially in the context of high glucose levels. PMID: 23747828
- Aged female L-Fabp-/- mice are protected against weight gain and hepatic steatosis. PMID: 22327204
- liver fatty acid-binding protein, the single most prevalent hepatic cytosolic protein that binds cholesterol, was upregulated twofold in SCP-2 null hepatocytes PMID: 22241858
- L-FABP gene ablation decreased fat oxidation and sensitized all mice to weight gain as whole body fat tissue mass (FTM) and LTM-with the most gain observed in FTM of control vs high-fat fed female L-FABP null mice. PMID: 20035485
- enhanced uptake and intracellular targeting of long and medium chain fatty acids to the nucleus PMID: 12023965
- L-FABP is an important determinant of hepatic lipid composition and turnover PMID: 12670956
- data point to an inducible defect in fatty acid utilization in fasted L-Fabp-/- mice that involves targeting of substrate for use in triglyceride metabolism PMID: 14534295
- under fasting conditions, hepatic L-FABP contributes to hepatic long chain fatty acid oxidation and ketogenesis by a nontranscriptional mechanism, whereas L-FABP can activate ketogenic gene expression in fed mice PMID: 14656998
- L-FABP may function as a carrier for selectively enhancing the distribution of long-chain fatty acyl CoA (LCFA-CoA), as well as LCFA, to nuclei for potential interaction with nuclear receptors. PMID: 14992586
- results with cultured primary hepatocytes isolated from L-FABP (+/+) and L-FABP (-/-) mice demonstrated a physiological role of L-FABP in the uptake and metabolism of branched-chain fatty acids PMID: 15155724
- gene expression of liver-type FABP was independent of PPARalpha and may have general implications for the activation of PPARgamma in alveolar macrophages PMID: 15203117
- Data show that liver fatty acid protein gene ablation exerts a significant role, especially in female mice, in branched-chain fatty acid metabolism. PMID: 15692150
- results suggesting a physiological role for the major cytosolic bile acid-binding protein (L-FABP) in influencing liver bile metabolic phenotype and gall-bladder bile lipids of male mice, especially in response to dietary cholesterol PMID: 15984932
- L-FABP is involved in the physiological regulation of cholesterol metabolism, body weight gain, and obesity. PMID: 16123197
- reducing both L-FABP and microsomal triglyceride transfer protein is an effective means to reduce very low density lipoprotein secretion without causing hepatic steatosis PMID: 16950764
- Inactivation of Gata4 or Hnf1alpha had a partial effect (approximately 50% reduction) on Fabp1 gene expression during cytodifferentiation and suckling. PMID: 17272516
- L-FABP can select cargo for and bud PCTV from intestinal ER membranes PMID: 17449472
- inhibition of CYP2E1 and regulation of L-FABP by Platycodi radix play an important role in alcohol-induced hepatoprotection PMID: 17587688
- L-Fabp(-/-) mice are protected against Western diet-induced obesity and hepatic steatosis. PMID: 18032478
- Knockout female C57BL mice exhibit increased obesity in aging. PMID: 18806093
- expression of renal hL-FABP was upregulated in the diabetic Tg mice and protective against tubulointerstitial damage of diabetic nephropathy PMID: 18854419
- role for L-FABP as an important physiological regulator of PPARalpha PMID: 19104910
- Together these data indicate a role for L-FABP in intestinal trafficking of both saturated (SFA),and cholesterol. PMID: 19116776
- Data suggest that changes in hepatic cholesterol metabolism and biliary lipid secretion as well as changes in enterohepatic BA metabolism increase gallstone susceptibility in LD fed L-Fabp(-/-) mice. PMID: 19136665
- studies support the hypothesis that L-FABP may facilitate ligand (LCFA)-activated PPARalpha transcriptional activity at least in part by increasing total LCFA ligand available to PPARalpha PMID: 19285478
- studies consistent with L-FABP regulating PPARalpha transcriptional activity in hepatocytes through direct interaction with PPARalpha; findings suggest role for L-FABP interaction with PPARalpha in long chain fatty acid metabolism PMID: 19289416
- renal expression and urinary excretion of hL-FABP significantly reflected the severity of tubulointerstitial damage in FA-induced nephropathy. PMID: 19435794
- Data support the hypothesis that L-FABP plays a role in physiological regulation of not only hepatic fatty acid metabolism, but also that of hepatic cholesterol. PMID: 19815623
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Cytoplasm.
-
蛋白家族:Calycin superfamily, Fatty-acid binding protein (FABP) family
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human HLA class II histocompatibility antigen gamma chain (CD74), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
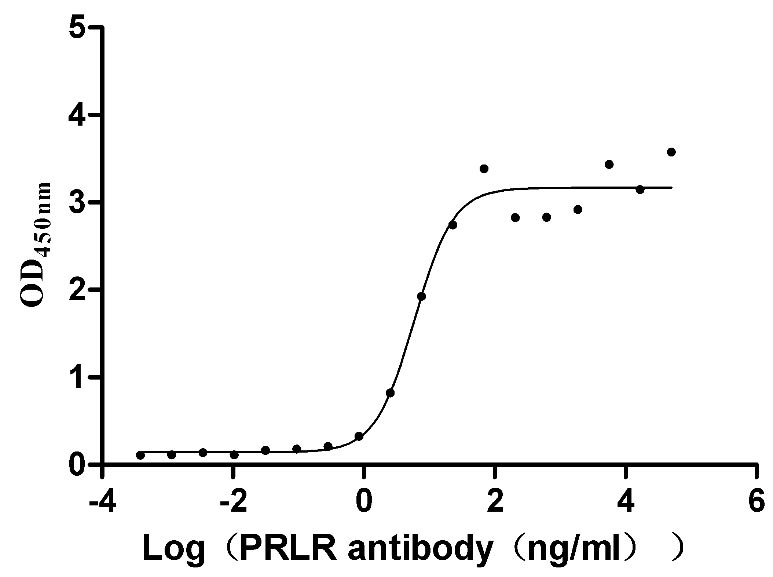
Recombinant Mouse Prolactin receptor (Prlr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
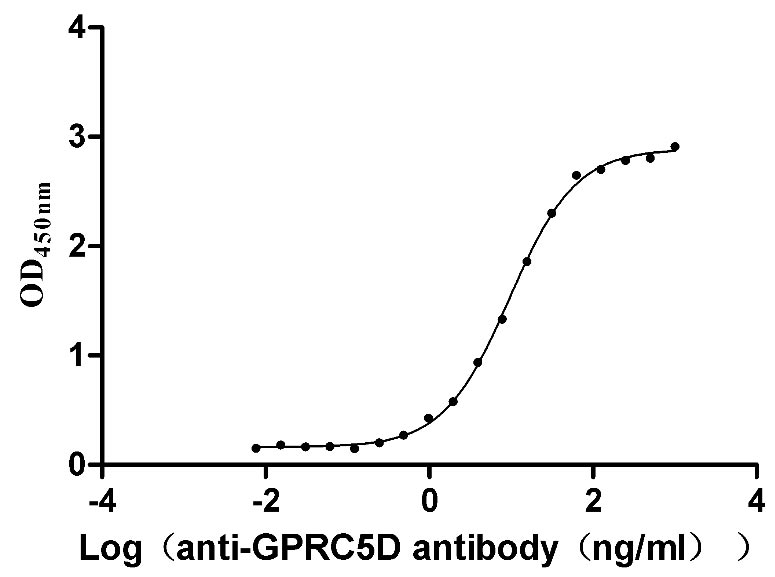
Recombinant Human G-protein coupled receptor family C group 5 member D (GPRC5D)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
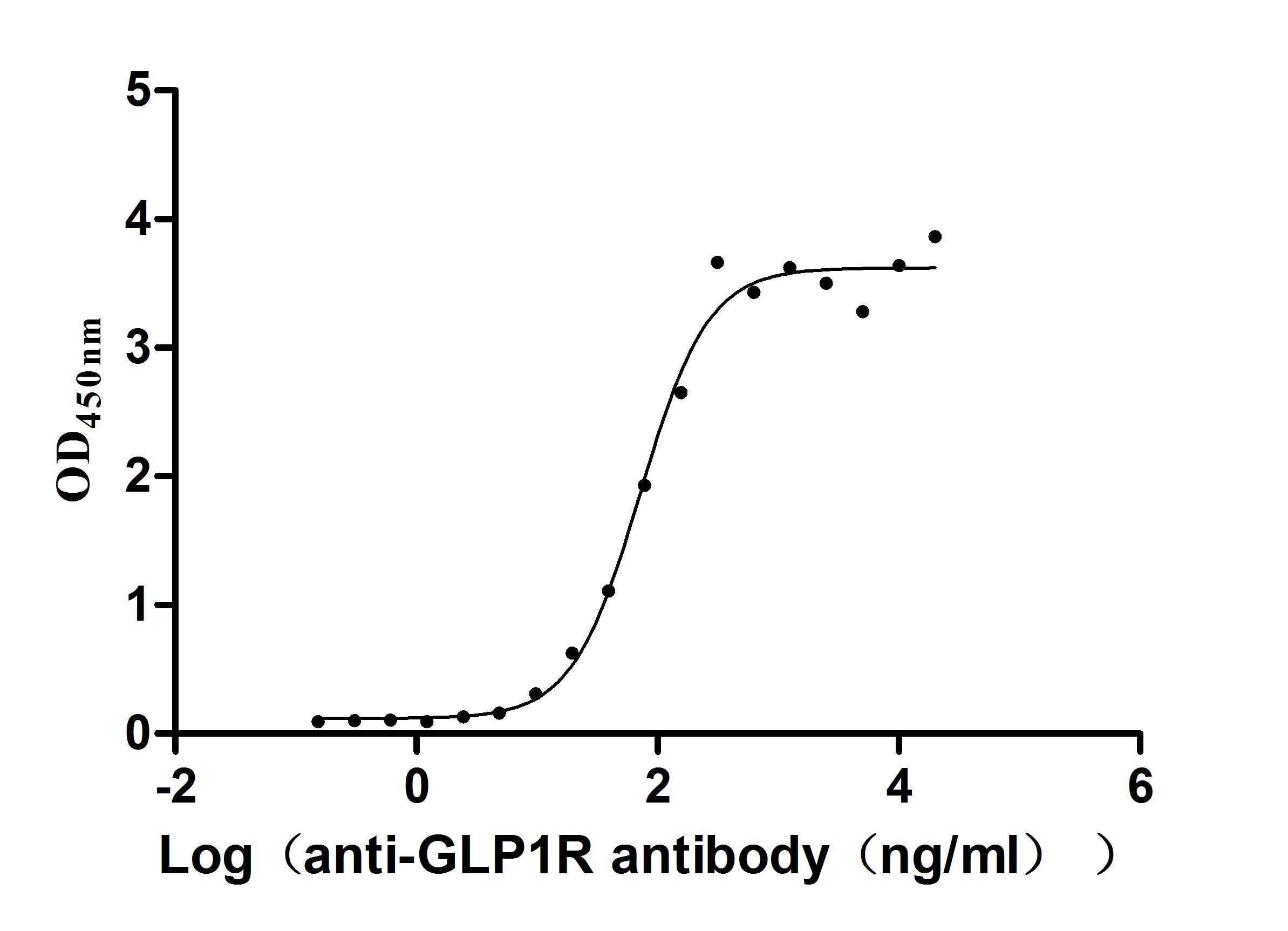
Recombinant Human Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP1R), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
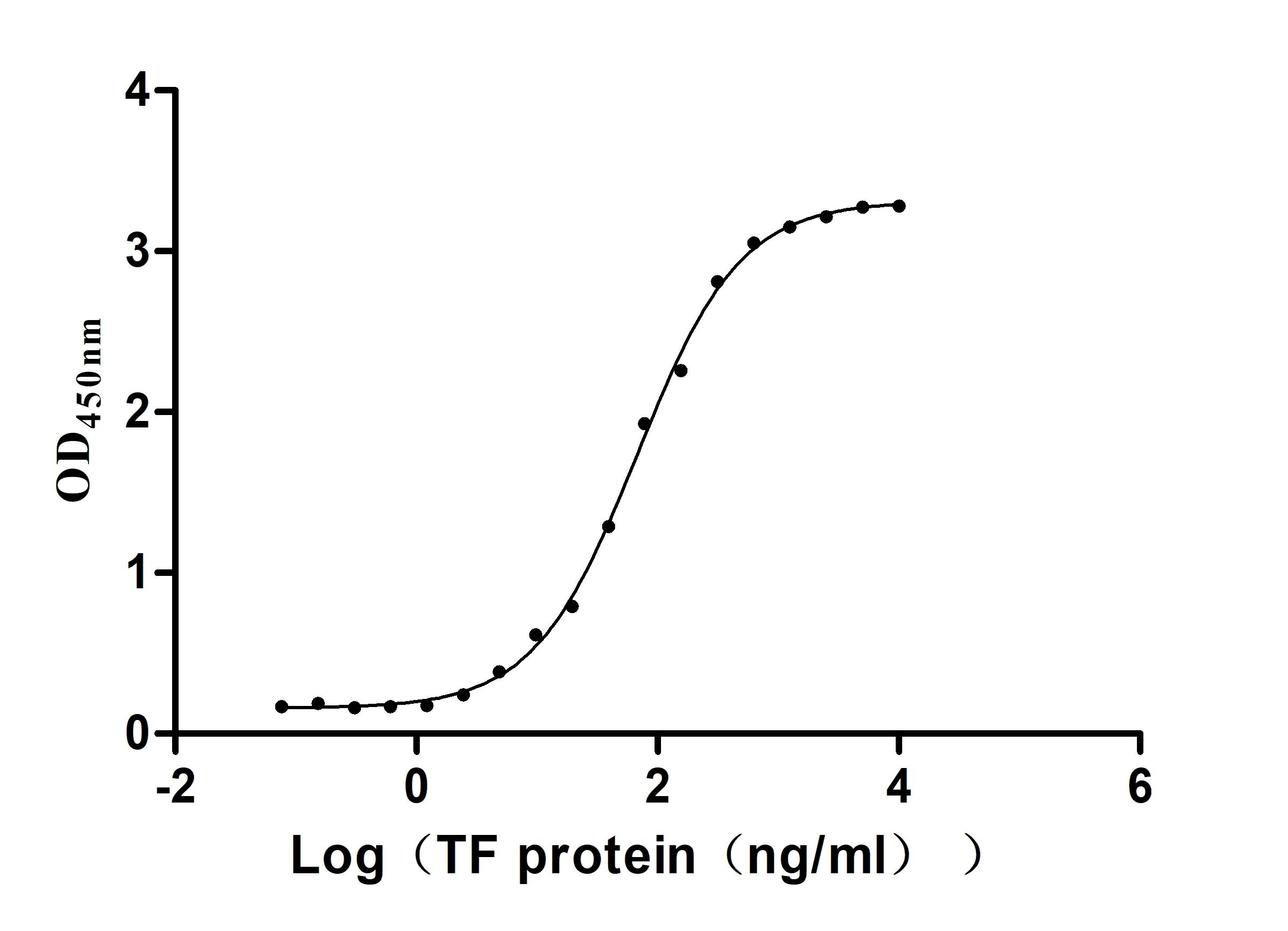
Recombinant Human Serotransferrin(TF) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
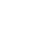
Recombinant Human Dipeptidase 3(DPEP3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



-AC1.jpg)