Recombinant Human ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 8 (ABCC8 HRINS SUR SUR1)
-
中文名稱:
-
貨號:CSB-EP2243HU-B
-
說明書:
-
規格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:ABCC8
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 8; Sulfonylurea receptor 1; ABCC8 HRINS SUR SUR1
-
種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白標簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Subunit of the beta-cell ATP-sensitive potassium channel (KATP). Regulator of ATP-sensitive K(+) channels and insulin release.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- Pancreatic differentiation of ABCC8-deficient cells recapitulated the congenital hyperinsulinism disease phenotype. PMID: 28600547
- HNF1A and ABCC8 are among the most frequently mutated maturity-onset diabetes of the young genes in south India. PMID: 29439679
- A lasso extension forms an interface between SUR1 and Kir6.2 adjacent to the ATP site in the propeller form and is disrupted in the quatrefoil form. These structures support the role of SUR1 as an ADP sensor and highlight the lasso extension as a key regulatory element in ADP's ability to override ATP inhibition. PMID: 29286281
- Combination of heterozygous mutations in the ABCC8 and KCNJ11 genes could also lead to beta cells dysfunction presenting as congenital hyperinsulinism. PMID: 29127764
- genetic association studies in pediatric population in Japan: Data confirm that mutations in KCNJ11 or ABCC8 are associated with neonatal diabetes mellitus. Novel mutations were identified; 2 in KCNJ11 (V64M, R201G) and 6 in ABCC8 (R216C, G832C, F1176L, A1263V, I196N, T229N). (KCNJ11 = ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel-11; ABCC8 = ATP-binding cassette subfamily C member-8) PMID: 27681997
- report two patients with neonatal diabetes in whom we unexpectedly identified recessively inherited ABCC8 p.Glu747 loss-of-function mutations PMID: 28663158
- In India, ABCC8 mutations were most common, with varied age of onset of diabetes, in our case series. PMID: 27496106
- The patient carries a heterozygous mutation c.2690A>T(p.D897V) of ABCC8 gene. PMID: 28777862
- Minor allele ABCC8 SNP genotypes have increased risk of cerebral edema, while major SNP alleles are protective in severe TBI. PMID: 27677908
- The p.A1369S variant is associated with a significantly lower risk of type 2 diabetes (odds ratio [OR] 0.93; 95% CI 0.91, 0.95; P = 1.2 x 10(-11)). The variant is associated with increased BMI (+0.062 kg/m(2); 95% CI 0.037, 0.086; P = 8.1 x 10(-7) PMID: 28411266
- Mutation in ABCC8 gene is associated with congenital hyperinsulinism. PMID: 28328534
- ABCC8 mutation causing loss of function of beta-cell KATP channels lead to congenital hyperinsulinism, higher basal [Ca(2+)] i and insulin secretion, increased insulin secretion in response to amino acids but not to glucose, increased basal rate of oxygen consumption and mitochondrial mass, increased rates of glycolysis, increased serine/glycine and glutamine biosynthesis, and low gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) levels. PMID: 28442472
- Hyperinsulinism-causing mutations cause multiple molecular defects in SUR1 nucleotide-binding domains. PMID: 28346775
- Genes ABCC7, A3, A8, A12, and C8 prevailed among the most upregulated or downregulated ones. In conclusion, the results supported our theory about general adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette gene expression profiles and their importance for cancer on clinical as well as research levels. PMID: 28468577
- Cross-linking experiments showed that KATP channel inhibitors promoted interactions between the N terminus of Kir6.2 and SUR1, whereas channel openers did not, suggesting the inhibitors enhance intersubunit interactions to overcome channel biogenesis and trafficking defects. PMID: 27573238
- Mutations of the ABCC8 gene is associated with congenital hyperinsulinism. PMID: 27682711
- ABCC8 mutation is associated with neonatal diabetes mellitus and iDEND syndrome. PMID: 27849623
- The most frequently seen mutations in Turkish patients with congenital hyperinsulinism (CHI) were ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 8 (ABCC8) gene, followed by 3-hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase (HADH) and kcnj11 channel (KCNJ11) genes. PMID: 27181376
- Mutations in the ABCC8 gene were the most common cause of congenital hyperinsulinism in our cohort. PMID: 26758964
- ABCC8 mutation is associated with persistently elevated insulin concentrations. PMID: 26581065
- A study of mutations in the ABCC8 gene that cause congenital hyperinsulinism demonstrate a clear functional distinction between SUR1 nucleotide-binding domain two (NBD2) and transmembrane domain (TMD) mutants PMID: 26092864
- up-regulation of SUR1 in humans point to this channel as one of the important molecular players in the pathophysiology of Post-traumatic brain contusions PMID: 26398596
- HNF1A gene mutations represented the second most frequent genetic cause of congenital hyperinsulinism of infancy in the Czech Republic PMID: 26431509
- single amino acid difference can account for the markedly different diazoxide sensitivities between channels containing either the SUR1 or SUR2A subunit isoforms. PMID: 26181369
- Mutations in ABCC8 are associated with neonatal diabetes mellitus. PMID: 25781672
- First description of a homozygous p.R1419H mutation in ABCC8 in a family leading to postprandial hyperglycemia followed by hypoglycemia. PMID: 25720052
- in a cohort of hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia patients from Isfahan, Iran, 78% were noted to have disease-causing mutations: 48% had HADH mutations and 26% had ABCC8 mutations. PMID: 26268944
- study investigated mutations in the KATP channel genes, allelic copy number and imprinting status at 11p15 in patients with congenital hyperinsulinism (CHI); found epigenetic alteration at the 11p15 region plays a central role in developing focal CHI by paternally derived mutations of the KATP channel and maternal allelic loss at this region PMID: 25765446
- genome-wide association studies in population of Pima Indians in Arizona: Data suggest that R1420H loss-of-function variant in ABCC8 is associated with higher birth weights and twofold increased risk for type 2 diabetes with 7-year earlier onset age. PMID: 26246406
- These calculations identified causal genetic variation within the ABCC8/KCNJ11 region for type 2 diabetes mellitus. PMID: 25955821
- Monoallelic ABCC8 mutations are a common cause of diazoxide-unresponsive diffuse form of congenital hyperinsulinism PMID: 24814349
- these data suggest an important role for the Sur1-Trpm4 channel in the pathophysiology of postischemic cell death PMID: 26172285
- Paternally inherited heterozygous ABCC8/KCNJ11 mutations can manifest as a wide spectrum of congenital hyperinsulinism. PMID: 25201519
- SUR1 alanine 1369 variant is associated with allelic susceptibility to TPP. PMID: 25143473
- Mutations in ABCC8 can cause Transient or Permanent Neonatal Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes secondary to mutations in ABCC8 often responds to sulfonylureas. PMID: 25456640
- Novel ABCC8 (SUR1) gene mutations in Asian Indian children with congenital hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. PMID: 25117148
- Activating ABCC8 mutations impaired the balance between beta and alpha cells in the patient, suggesting an effect on beta-cell mass development. PMID: 24941889
- Homozygous mutation in the ABCC8 gene is associated with congenital hyperinsulinism. PMID: 24945427
- Paternally inherited monoallelic mutations of ABCC8 and KCNJ11 are likely the main causes of KATP-congenital hyperinsulinism in Chinese patients. PMID: 25008049
- after a molecular analysis of the ABCC8 gene revealed a novel heterozygous missense mutation in neonatal diabetes mellitus PMID: 24468609
- Clinical and genetic evaluation of patients with KATP channel mutations from the German registry for congenital hyperinsulinism. PMID: 24401662
- Mutations in ABCC8 and KCNJ11 are common causes of CHI in Chinese patients. Mutation analysis showed more novel and monoallele mutations in KATP genes. PMID: 24434300
- All patients were genotyped for CYP2C9, KCNJ11 and ABCC8. PMID: 24442125
- the review summarizes the current evidence of contribution of ABC8 genetic variants to the development of Diabetes mellitus (Review) PMID: 24768178
- This is the largest study to report genotype-phenotype correlations among Turkish patients with congenital hyperinsulinism (CHI). Mutations in ABCC8 and KCNJ11 are the commonest causes of CHI in Turkish patients (48.6%). PMID: 24686051
- Octreotide-induced long QT syndrome in a child with congenital hyperinsulinemia and a novel missense mutation (p.Met115Val) in the ABCC8 gene PMID: 24080777
- Homozygous mutations in ABCC8 are the most common causes of CHI in Saudi patients PMID: 24145932
- Forty-one case-control association studies of KCNJ11 and ABCC8 polymorphisms with type 2 diabetes, including 61,879 subjects, were identified and used in our meta-analysis PMID: 24065655
- molecular analysis of the ABCC8 gene revealed a heterozygous mutation (p.Arg837X) in a newborn with hyperinsulinism and also in his 29-year-old asymptomatic father PMID: 23301914
- We found three missense homozygous mutations in the ABCC8 coding region of patients with congenital hyperinsulinism of infancy. One mutation is novel (G1554D, whereas R526C and P1413L mutation have been previously described as causative PMID: 23652837
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關疾病:Leucine-induced hypoglycemia (LIH); Familial hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia 1 (HHF1); Diabetes mellitus, permanent neonatal (PNDM); Transient neonatal diabetes mellitus 2 (TNDM2)
-
亞細胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:ABC transporter superfamily, ABCC family, Conjugate transporter (TC 3.A.1.208) subfamily
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Glucagon receptor (GCGR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Dog Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (CRTAM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1(TM4SF1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
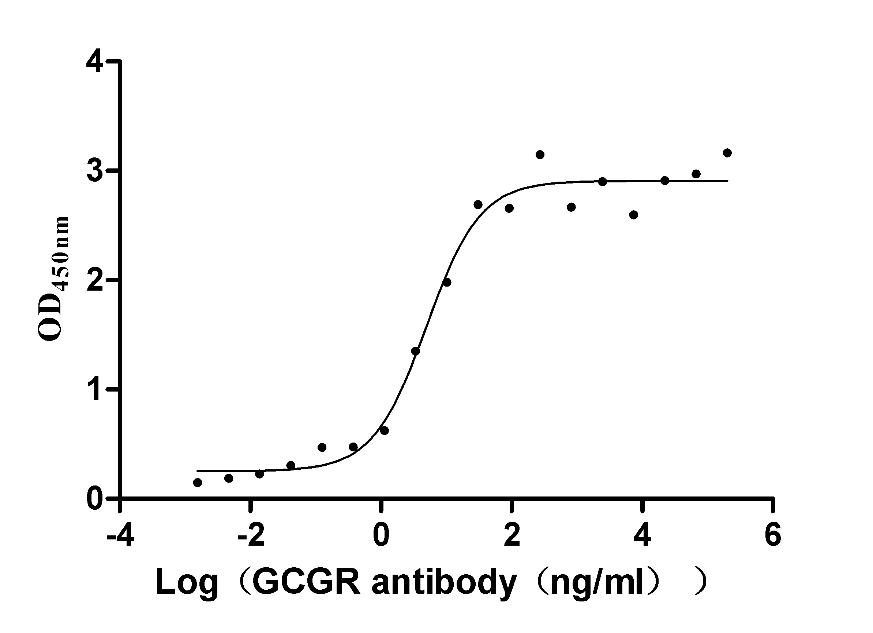
Recombinant Human Cadherin-1(CDH1),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)