Recombinant Mouse Eyes absent homolog 1 (Eya1)
-
中文名稱:小鼠Eya1重組蛋白
-
貨號:007906MO
-
規格:20μg/100μg/1mg(1mg*1 or 500ug*2)
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
別名:Eya1; Eyes absent homolog 1; EC 3.1.3.16; EC 3.1.3.48
-
Uniprot No.:
-
種屬:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
測定原理:N-terminal His-tagged/Tag-Free
-
測定方法:Full length protein
-
儲存條件:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
靶點詳情
-
功能:Functions both as protein phosphatase and as transcriptional coactivator for SIX1, and probably also for SIX2, SIX4 and SIX5. Tyrosine phosphatase that dephosphorylates 'Tyr-142' of histone H2AX (H2AXY142ph) and promotes efficient DNA repair via the recruitment of DNA repair complexes containing MDC1. 'Tyr-142' phosphorylation of histone H2AX plays a central role in DNA repair and acts as a mark that distinguishes between apoptotic and repair responses to genotoxic stress. Its function as histone phosphatase may contribute to its function in transcription regulation during organogenesis. Has also phosphatase activity with proteins phosphorylated on Ser and Thr residues (in vitro). Required for normal embryonic development of the craniofacial and trunk skeleton, kidneys and ears. Together with SIX1, it plays an important role in hypaxial muscle development; in this it is functionally redundant with EYA2.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- Notch is regulated by the threonine phosphatase activity of Eya1. Eya1 dephosphorylates p-threonine-2122 of the Notch1 intracellular domain (Notch1 ICD), which increases the stability of Notch1 ICD and maintains Notch signaling activity in the non-neuronal epibranchial placodal cells. PMID: 29140246
- data support a model where Eya-Six may form a complex to regulate nephron progenitor cell development before metanephric specification and are critical mesenchymal factors for inducing nephric duct development. PMID: 25903664
- Eya1 phosphatase promotes Shh signaling during hindbrain development and oncogenesis PMID: 25816987
- results reveal a functional link between Eya1, Six2, and Myc in driving the expansion and maintenance of the multipotent progenitors during nephrogenesis PMID: 25458011
- BOR syndrome-associated Eya1 missense mutations S454P, L472R, and L550P lead to enhanced proteasomal degradation of the Eya1 protein. PMID: 24489909
- these findings reveal that the canonical Wnt and PI3K/Akt signal pathways restrain the GSK3/Fbw7-dependent Eya1 ubiquitination, and they further suggest that dysregulation of this novel axis contributes to tumorigenesis. PMID: 24752894
- The EYA1 phosphatase regulates cell-cycle control via transcriptional complex formation at the cyclin D1 promoter. PMID: 23636126
- These findings uncover novel functions for Six1-Eya1-SHH pathway during the saccular phase of lung morphogenesis. PMID: 23895934
- EYA1 is efficiently degraded during mitotic exit in a ANAPC1-dependent manner and these two proteins physically interact. PMID: 23263983
- EYA1 and SIX1 drive the neuronal developmental program in cooperation with the SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling complex and SOX2 in the mammalian inner ear. PMID: 22513373
- Deletion of either or both Six1 and Eya1 genes results in genitourinary tract defects including persistent cloaca; hypospadias; and hypoplastic genitalia. PMID: 21968101
- Six1 and Eya1 genetically interacted with Fgf8 and the Tbx1 pathway that is crucial for cardiovascular and craniofacial morphogenesis PMID: 21364285
- Eya1 function is critical for proper coordination of lung epithelial, mesenchymal and vascular development. PMID: 21129374
- Data report the identification of the related proteins Sipl1 (Shank-interacting protein-like 1) and Rbck1 (RBCC protein interacting with PKC1) as novel interaction partners of Eya1. PMID: 20956555
- Eya1 IS required for normal ear develoPMENT PMID: 11804780
- Impaired interactions between mouse Eyal harboring mutations found in patients with branchio-oto-renal syndrome and Six, Dach, and G proteins PMID: 11950062
- Eya1 is required for the morphogenesis of mouse thymus, parathyroid and thyroid. PMID: 12070080
- Data identify Six1 and Eya1 as the first transcriptional complex that is able to reprogram adult slow-twitch oxidative fibers toward a fast-twitch glycolytic phenotype. PMID: 15226428
- constructs of the homologous region ( Eya1HR and Eya4HR) interact with Six1 prey constructs, although no interaction with Dach1 prey was demonstrable PMID: 15492887
- During the development of epibranchial placode-derived distal cranial sensory ganglia, while the phenotype appears less severe in Six1 than in Eya1 mutants PMID: 15496442
- Eya1 signaling is critical to the normal expression patterns of Tbx1, Ngn1, and NeuroD in the developing mouse otocyst PMID: 15817220
- Eya1 acts as a critical regulator for specifying the metanephric mesenchyme. PMID: 16018995
- essential role for Eya1 and Six genes in patterning the third pouch into organ-specific primordia PMID: 16530750
- Branchio-oto-renal syndrome (BOR)-associated mutations lead to a loss of phosphatase activity in Eya1 proteins, while mutations associated with ocular defects yield Eya1 proteins with near normal levels of phosphatase activity. PMID: 16797546
- These results show that, while Eya1 exerts an early function essential for normal growth and patterning of the otic epithelium, it also functionally synergizes with Pax2 during the morphogenesis of all sensory areas of mammalian inner ear. PMID: 16916509
- Eya1 protein is required for hypaxial somitic myogenesis in the mouse embryo PMID: 17098221
- Eya1 activity, in a concentration-dependent manner, plays a key role in the regulation of genes known to be important for sensory development PMID: 18678597
- phosphatase activity of a number of variants of the mouse Eya1 protein that harbours single point mutations that were associated with branchio-oto-renal syndrome (BOR), branchio-oto syndrome (BO) and ocular defects, respectively, in humans PMID: 18759246
- a comprehensive group of enhancers around Eya1 locus, which are probably involved in the control of the complex expression pattern of Eya1 in vivo. PMID: 18816442
- Mapping of genetic modifiers of Eya1 ( bor/bor ) in CAST/EiJ and BALB/cJ that suppress cochlear aplasia and associated deafness. PMID: 18836772
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關疾病:A spontaneous mutation leading to decreased Eya1 expression gives rise to the Eya1-bor phenotype. It is characterized by circling behavior and deafness, due to gross morphological abnormalities of the inner ear, and dysmorphic or missing kidneys. This autosomal recessive trait resembles human branchio-oto-renal (BOR) syndrome.
-
亞細胞定位:Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:HAD-like hydrolase superfamily, EYA family
-
組織特異性:Extensively expressed in cranial placodes, branchial arches, CNS and developing eye and nose.
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human HLA class II histocompatibility antigen gamma chain (CD74), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
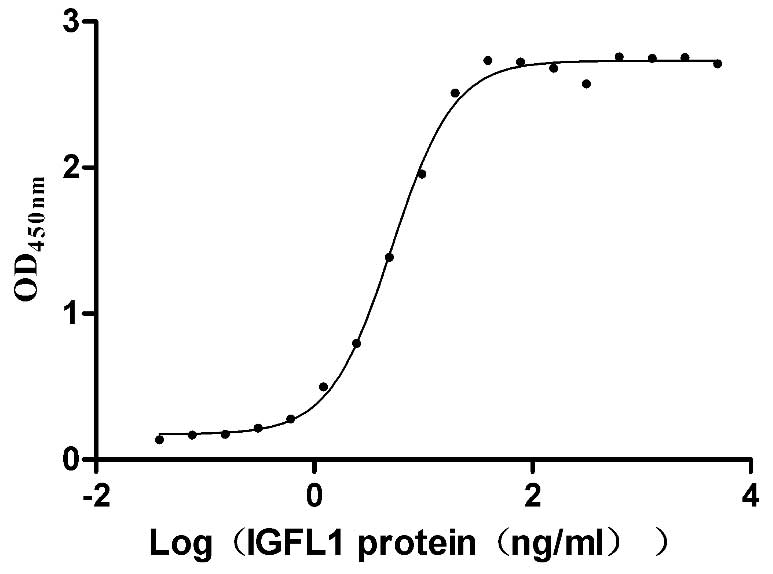
Recombinant Human IGF-like family receptor 1 (IGFLR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
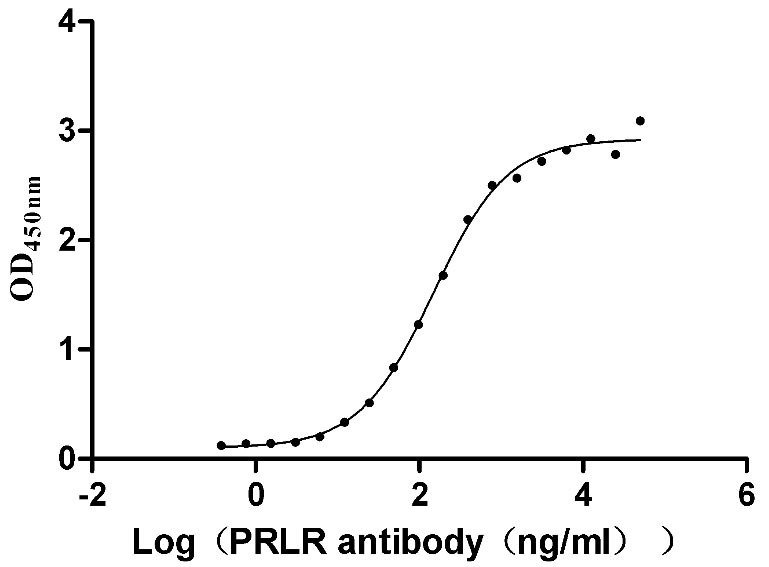
Recombinant Human Prolactin receptor (PRLR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
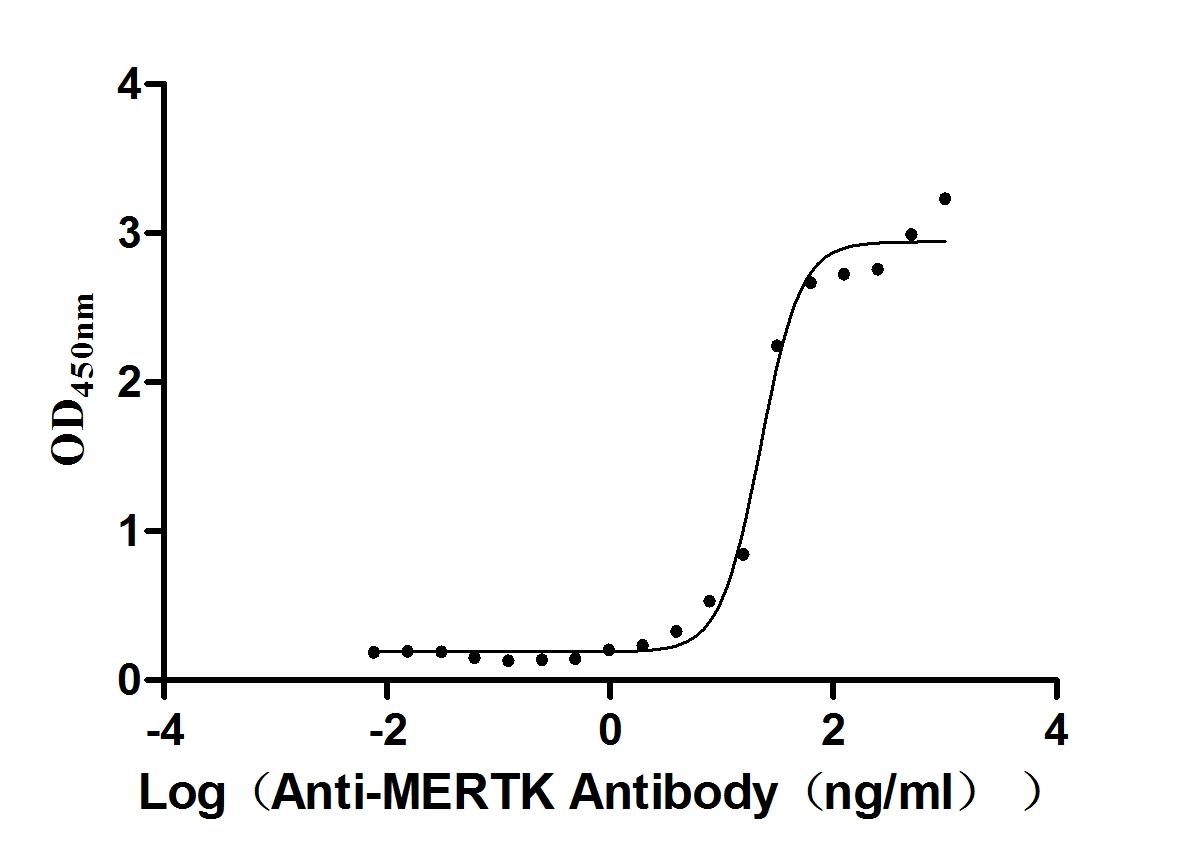
Recombinant Mouse Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer (Mertk), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
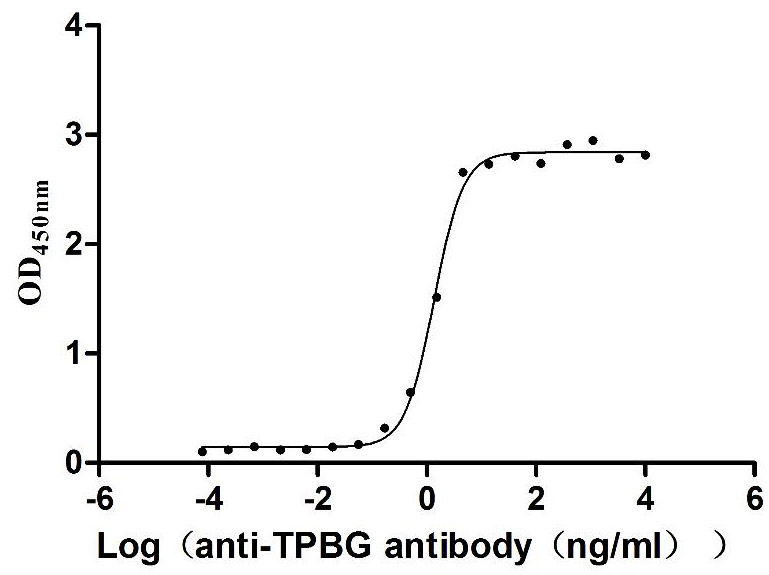
Recombinant Human Trophoblast glycoprotein (TPBG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
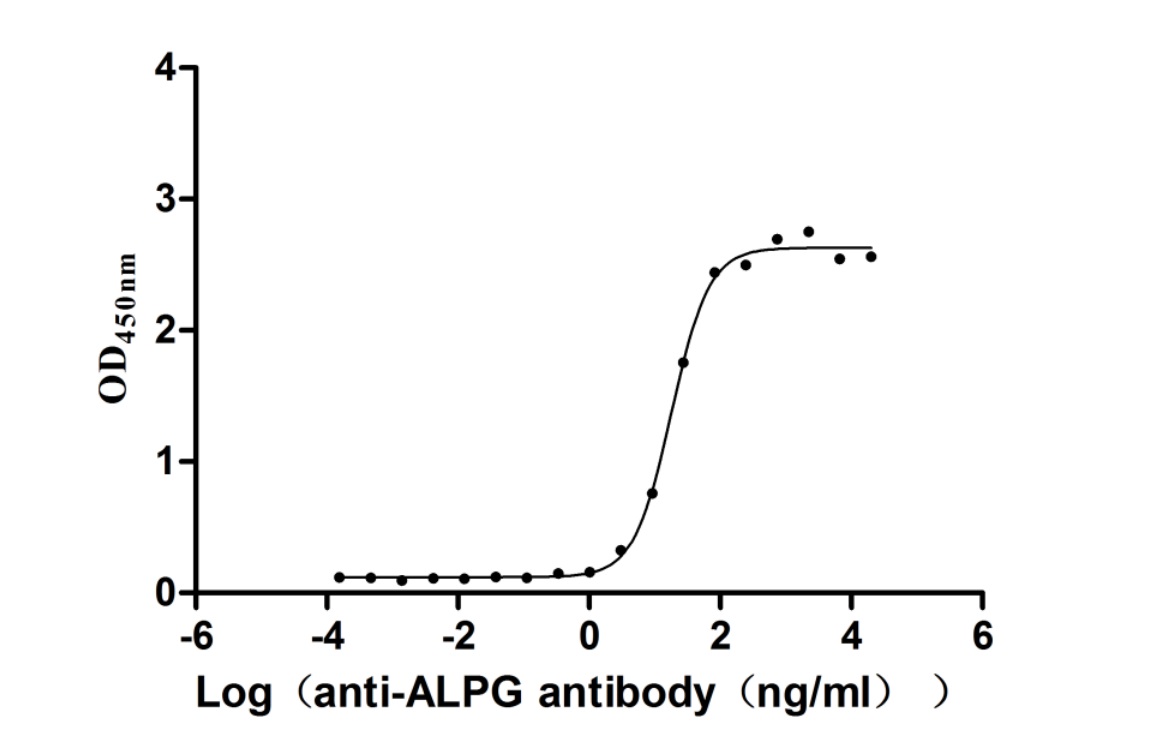
Recombinant Human Alkaline phosphatase, germ cell type (ALPG) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
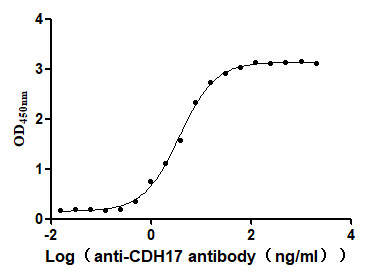
Recombinant Human Cadherin-17 (CDH17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



-AC1.jpg)